-
 新闻动态
新闻动态
-
查看更多

-
 于珏等:How Much Does Syntactic Complexity Contribute to the Oral Narrative Performance of Prelingually Deaf Mandarin-Speaking Children With Cochlear Implants?
于珏等:How Much Does Syntactic Complexity Contribute to the Oral Narrative Performance of Prelingually Deaf Mandarin-Speaking Children With Cochlear Implants? 01-07
01-07
-
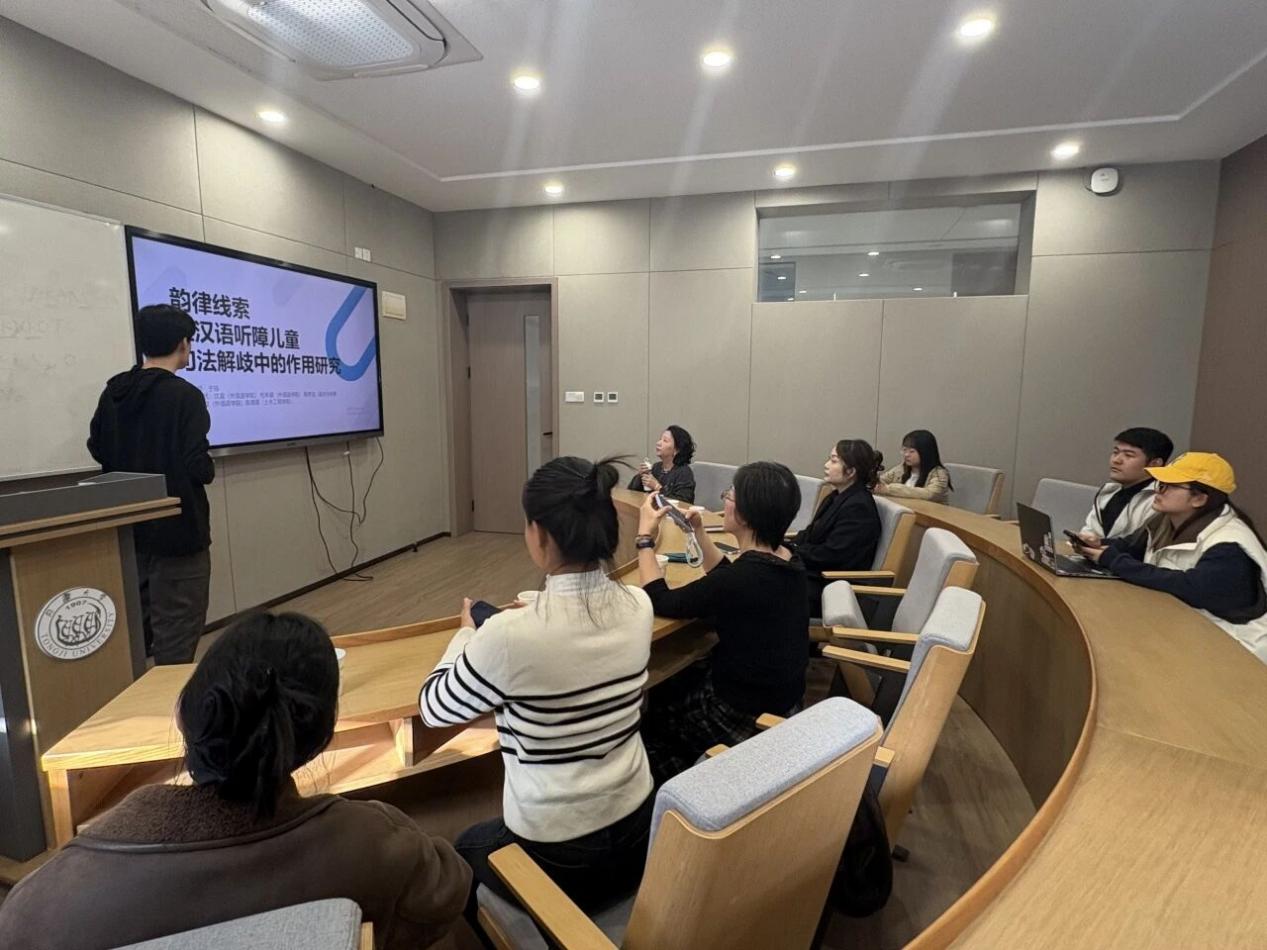 上海市第一聋哑学校校长一行走进同济大学言语-语言加工中心开展深度交流
上海市第一聋哑学校校长一行走进同济大学言语-语言加工中心开展深度交流 01-07
01-07
-
 益语团队“儿童听觉工作记忆测试软件”获国家专利批准
益语团队“儿童听觉工作记忆测试软件”获国家专利批准 01-07
01-07
-
 王婷、Yong-cheol Lee:Ranking the acoustic cues of contrastive focus in Taiwan Mandarin: Evidence from number words
王婷、Yong-cheol Lee:Ranking the acoustic cues of contrastive focus in Taiwan Mandarin: Evidence from number words 01-04
01-04
-
2026-01-04蒋宇涵、王婷:Speech prosody and pragmatic scalar inferences: Divergent cognitive strategies in adults with high and low levels of autistic traitsAbstract: BackgroundGiven the communicative challenges associated with autistic traits (ATs), individuals with higher levels of ATs can sometimes make certain pragmatic inferences, such as quantifier scalar implicatures. However, it remains unclear whether they can effectively integrate prosodic cues when drawing these inferences.MethodsThis study examines scalar quantifier interpretations and reaction time (RT) among Mandarin-speaking adults using computer-based Picture-Sentence Judgment Selec
-
2025-12-22赵信娴、Aine Ito、杨小虎:Contributions of Language-Specific and Domain-General Cognitive Abilities to the Comprehension of Focus Prosody in Jianghuai Mandarin: Effects of AgeAbstract A growing body of research has explored the cognitive factors influencing aging adults’ recognition of spoken words and phrases. In contrast, research on the cognitive contributions to speech prosody comprehension in tonal languages across adulthood remains relatively limited. This study aimed to bridge this gap by investigating the contributions of language-specific and domain-general cognitive factors to focus prosody comprehension performance among aging speakers of Jianghuai Mand
-
2025-12-11王培娟、常欣:Language adaptation of international immigrants: connotation and dimensionsAbstract:International immigrants’ adaptation to language life and satisfaction of their linguistic demands are precondition for successful integration into the host country’s society. However, current theories and studies on immigrants’ language adaptation are insufficient to support further research on the language adaptation of international immigrants in the host country. This study elucidates the connotation of language adaptation among international immigrants and its three structural dime
-
2025-12-09我中心博士生荣获第三届“赵元任语言实验之星”奖近日,经过来自全国各高校和研究机构的三十多位语言实验专家严肃认真的评审以及评选委员会的认真审议,第三届“赵元任语言实验之星”于2025年12月4日评选出7获奖者和7提名奖。我院言语-语言加工研究中心2023级博士生蒋宇涵荣获第三届“赵元任语言实验之星”提名奖。在王婷副教授的指导下,蒋宇涵同学于2025年4月在Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders发表论文“Prosodic Focus Effects on Covert “Only” Reading of Scalar Quantifiers in Autistic and Non-autistic Children Under Tonal Language Background”。该论文从韵律焦点这一语言现象切入,探讨了其对汉语孤独症儿童与典型发展儿童理解量词意义的影响。研究发现,孤独症儿童在处理韵律信息与语用解读的交互时,表现出独特的加工特点,且个体认知差异在这一过程中起着重要作用。该成果为发展更具针对性的干预策略提供了新的视角和实证支持。“赵元任语言实验之星”奖由《实验语言学》编
-
2025-11-24刘文翠、杨小虎:上海市区方言中韵母[i]-[iɪ]的语音演变调查摘要:本研究基于词汇扩散理论框架,采用问卷调查法,对上海市区方言中韵母[i]-[iɪ]的语音区分状况展开考察。研究结果显示,上海市区方言中韵母[i]、[iɪ]相关词汇的读音仍然存在不同程度的区分,不同人群之间存在年龄差异和性别差异:老年说话人[i]-[iɪ]区分程度显著高于中年说话人;男性说话人的[i]-[iɪ]区分程度显著高于女性说话人。同时,不同声母类型的词汇在音变过程不同步,唇音声母音节的音变相对缓慢,而齿音声母音节和腭音声母音节的音变较为迅速。总体而言,上海市区方言韵母[i]-[iɪ]尚未完成音系合并,仍处于动态演变过程中。原载《实验语言学》2025年14卷第3号,45-52。









